基本的な英語文法は、英語を正確かつ効果的に使用するための規則の体系です。基本的な英語文法をマスターすることで、リスニング、スピーキング、リーディング、ライティングのスキルが向上します。以下の記事では、MochiMochiが基本的な英語文法をまとめ、実践的な練習問題も提供しています。ぜひご覧いただき、実践してみてください!
英語の時制
現在形
現在形
1. 動詞の基本形の場合:
肯定文:
S + V (s,es)
否定文:
S + don’t/ doesn’t + V
疑問文:
Do/ Does + S + V?
例:
I play tennis every weekend. (私は毎週末テニスをします)
He does not (doesn’t) go to the gym. (彼はジムに行きません)
Do you like ice cream? (あなたはアイスクリームが好きですか?)
2. 動詞 “to be” の場合
肯定文:
I + am
He/She/It + is
You/We/They + are
否定文:
I + am not
He/She/It + is not (isn’t)
You/We/They + are not (aren’t)
疑問文:
Am + I?
Is + He/She/It?
Are + You/We/They?
例:
I am a doctor. (私は医者です)
He isn’t a student. (彼は学生ではありません)
Are they friends? (彼らは友達ですか?)
使い方
- 明白な事実や真理を表す
例: The sun rises in the east. (太陽は東から昇る)
- 習慣や繰り返される行動を表す
例: She goes to the gym every day. (彼女は毎日ジムに行く)
- スケジュールや時間表を表す(通常は、電車や飛行機の予定など事前に決まっているイベントに使う)
例: The train leaves at 6 p.m. (電車は午後6時に出発する)
- 現在の状態や状況を表す
例: I live in New York. (私はニューヨークに住んでいる)
練習問題
括弧内の動詞の正しい形を空欄に記入しなさい:
a. He _____ (go) to school by bus.
b. We _____ (not/play) video games.
c. _____ (you/enjoy) reading books?
d. She _____ (not/like) coffee.
e. They _____ (live) in New York.
答え:
a. He goes to school by bus.
b. We do not (don’t) play video games.
c. Do you enjoy reading books?
d. She does not (doesn’t) like coffee.
e. They live in New York.
MochiVocabで効果的に英語の単語を学ぶ
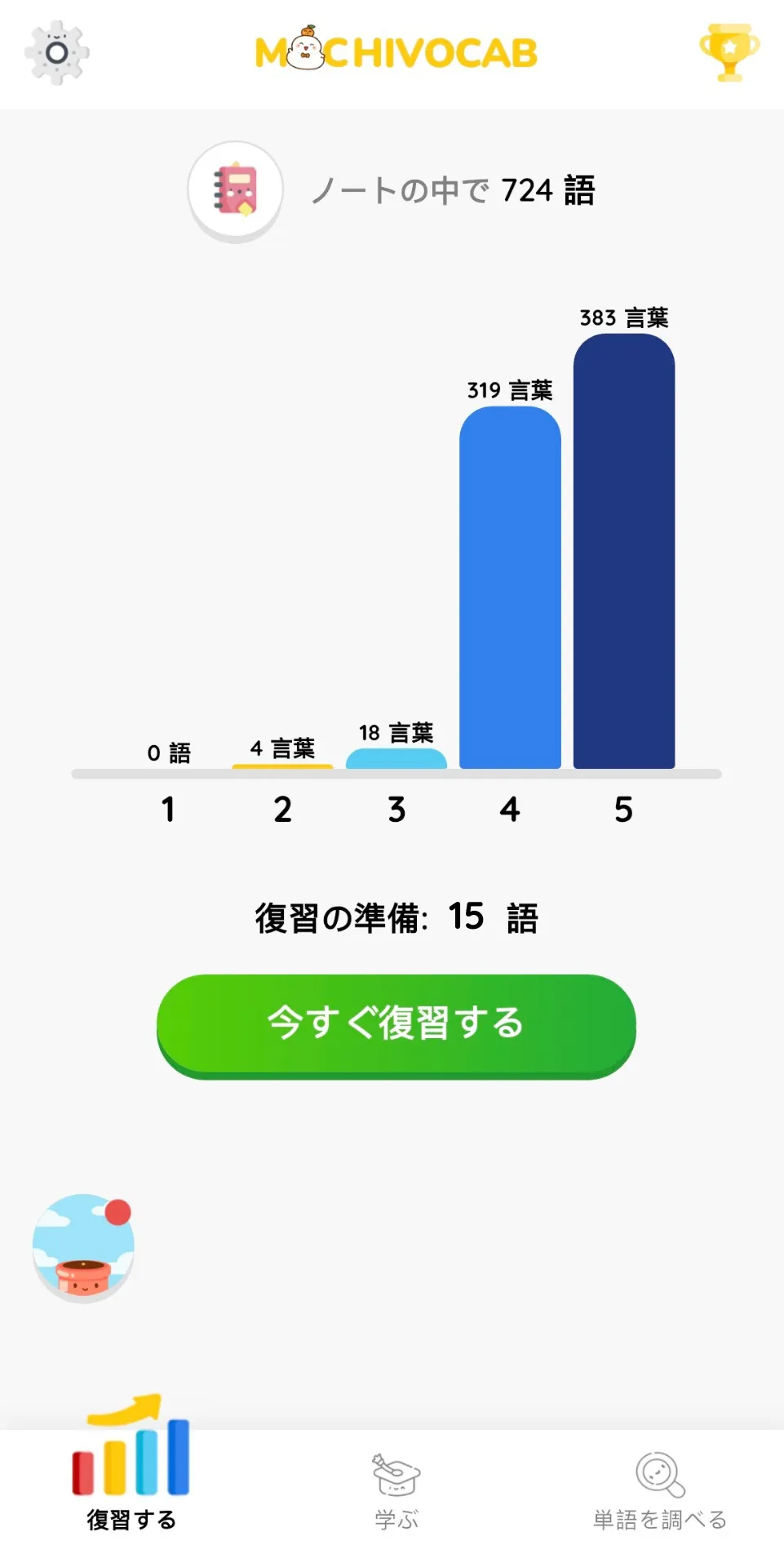
MochiVocabは、スペース・レピティション(間隔反復)という方法を使用して、ユーザーの学習履歴を分析し、「ゴールデンタイム」を計算して、ユーザーが知識を忘れそうな時に復習を促すアプリです。毎日10〜15分だけで、MochiVocabは1か月で最大1000語の単語を記憶するのを助けます。
あなたの学習履歴に基づいて、MochiVocabはあなたが学習した単語を5つの記憶レベルに分けて整理します。高いレベルの単語は復習間隔が長くなります。一方、低いレベルの単語は頻繁に復習を促され、あなたが確実に記憶するまで続けられます。これにより、既に覚えた単語の復習時間を減らし、覚えにくい単語に集中できます。

現在進行形
構文
肯定文:
S + am/is/are + V-ing
否定文:
S + am not/isn’t/aren’t + V-ing
疑問文:
Am/Is/Are + S + V-ing?
例:
He is playing football now. (彼は今サッカーをしています)
They aren’t doing their homework. (彼らは宿題をしていません)
Are you cleaning the kitchen? (あなたは台所を掃除していますか?)
使い方
- 話している時点での出来事
例: I’m watching TV now. (私は今テレビを見ています)
- alwaysを使ってイライラや不満を表現する場合
例: She is always borrowing my money. (彼女はいつも私のお金を借ります)
- 将来確実に起こる出来事
例: He’s flying to London next week. (彼は来週ロンドンに飛びます)
- 短期間や一時的な出来事
例: This week Paul is traveling to work by bus because his car breaks down. (今週、ポールは車が故障したためバスで通勤しています)
練習問題
括弧内の動詞の正しい形を空欄に記入しなさい:
a. He _____ (write) a letter.
b. We _____ (not/play) video games.
c. _____ (you/watch) TV?
d. She _____ (not/eat) lunch.
e. They _____ (have) a meeting.
答え:
a. He is writing a letter.
b. We are not (aren’t) playing video games.
c. Are you watching TV?
d. She is not (isn’t) eating lunch.
e. They are having a meeting.
過去形
構文
1. 動詞の基本形の場合:
肯定文:
S + V (-d/ed/ied/不規則変化)
否定文:
S + didn’t + V
疑問文:
Did + S + V?
例:
I visited my grandparents last weekend. (私は先週末に祖父母を訪ねました)
She did not (didn’t) watch a movie yesterday. (彼女は昨日映画を見ませんでした)
Did they play soccer after school? (彼らは放課後サッカーをしましたか?)
2. 動詞 “to be” の場合:
肯定文:
I/He/She/It + was
You/We/They + were
否定文:
I/He/She/It + was not
You/We/They + were not
疑問文:
Was + I/He/She/It?
Were + You/We/They?
例:
I was at home last night. (私は昨晩家にいました)
They were not (weren’t) happy yesterday. (彼らは昨日幸せではありませんでした)
Were they tired after the trip? (彼らは旅行後に疲れていましたか?)
使い方
- 過去に起こり、終了した出来事
例: He sold his car two weeks ago. (彼は2週間前に車を売りました)
- 過去に連続して起こった出来事
例: She put on her coat, took her bag and left the house. (彼女はコートを着て、バッグを持って家を出ました)
- 過去に起こり、もう二度と起こらない行動
例: I once spoke to Princess Diana. She passed away years ago. (かつてダイアナ妃と話したことがあります。彼女は数年前に亡くなりました)
練習問題
括弧内の動詞の正しい形を空欄に記入しなさい:
a. She _____ (open) the door and _____ (enter) the room.
b. We _____ (not/see) the movie last weekend.
c. _____ (you/go) to the party last night?
d. He _____ (not/buy) a new car.
e. They _____ (visit) their grandparents last summer.
答え:
a. She opened the door and entered the room.
b. We did not (didn’t) see the movie last weekend.
c. Did you go to the party last night?
d. He did not (didn’t) buy a new car.
e. They visited their grandparents last summer.
過去進行形
構文
肯定文:
S + was/were + V-ing
否定文:
S + wasn’t/weren’t + V-ing
疑問文:
Was/Were + S + V-ing?
例:
I was reading a book when you called. (あなたが電話したとき、私は本を読んでいました)
They were not (weren’t) playing soccer in the park. (彼らは公園でサッカーをしていませんでした)
Were we having dinner at that time? (私たちはその時夕食を食べていましたか?)
使い方
- 過去の特定の時点で起こっていた行動
例: Jenny was preparing for her Math exam at 8PM last night. (昨夜の8時にジェニーは数学の試験の準備をしていました)
- 過去に同時に起こっていた行動 (while を使う)
例: While the children were reading books, the cat was playing with its yarn. (子供たちが本を読んでいる間、猫は毛糸玉で遊んでいました)
- 過去に行動が進行中に別の行動が割り込んできた場合 (割り込む行動は過去形を使う)
例: I burnt my hand while I was making an omelet. (オムレツを作っているときに手を火傷しました)
練習問題
括弧内の動詞の正しい形を空欄に記入しなさい:
a. She _____ (write) a letter when the phone rang.
b. We _____ (not/play) video games at 5 p.m. yesterday.
c. _____ (you/watch) TV when I called?
d. He _____ (not/eat) lunch when you arrived.
e. They _____ (have) a meeting at that time.
答え:
a. She was writing a letter when the phone rang.
b. We were not (weren’t) playing video games at 5 p.m. yesterday.
c. Were you watching TV when I called?
d. He was not (wasn’t) eating lunch when you arrived.
e. They were having a meeting at that time.
未来形
構文
肯定文:
S + will + V
否定文:
S + won’t + V
疑問文:
Will + S + V?
例:
I will visit my grandparents next weekend. (私は来週末に祖父母を訪ねます)
She will not (won’t) watch a movie tonight. (彼女は今夜映画を見ません)
Will he study hard for the exam? (彼は試験のために一生懸命勉強しますか?)
使い方
- 計画していない未来の予測
例: In 2030, people will travel by flying cars. (2030年には、人々は空飛ぶ車で移動するでしょう)
- 即座の決定
例: I know. I’ll go to China next summer. (わかりました。来年の夏に中国に行きます)
- 誰かのために何かをする提案や要求
例: We’ll help you to get ready for your holiday. (私たちはあなたの休暇の準備を手伝います)
- 自分では制御できない未来の出来事
例: Lisa will be 14 years old next week. (リサは来週14歳になります)
練習問題
括弧内の動詞の正しい形を空欄に記入しなさい:
a. She _____ (open) the door and _____ (enter) the room.
b. We _____ (not/play) video games tonight.
c. _____ (you/go) to the party next Saturday?
d. He _____ (not/buy) a new car.
e. They _____ (visit) their grandparents next summer.
答え:
a. She will open the door and will enter the room.
b. We will not (won’t) play video games tonight.
c. Will you go to the party next Saturday?
d. He will not (won’t) buy a new car.
e. They will visit their grandparents next summer.
受動態
構造
能動態:
S + V + O
受動態:
S + to be + p2 + by O
例:
She (S) wrote (V) the novel (O). (彼女がその小説を書いた)
→ The novel (S) was written (to be + p2) by her (by O). (その小説は彼女によって書かれた)
能動態から受動態への変換方法
- 能動態の主語 (S)、動詞 (V)、目的語 (O) を確認する。
- 能動態の時制を確認し、その時制に対応する be動詞 を確認する。
- 上記の公式に従って文を変換する。
能動態から受動態への動詞変換方法
- 現在形: am/is/are + 過去分詞
- 現在進行形: am/is/are being + 過去分詞
- 現在完了形: have/has been + 過去分詞
- 過去形: was/were + 過去分詞
- 過去進行形: was/were being + 過去分詞
- 過去完了形: had been + 過去分詞
- 未来形: will be + 過去分詞
- 未来完了形: will have been + 過去分詞
- be going to: am/is/are/was/were + going to be + 過去分詞
- 助動詞 (can, should, mustなど): 助動詞 + be + 過去分詞
練習問題
次の文を受動態に変換してください:
1. They built a new bridge across the river.
2. Someone will clean the room later.
3. The teacher is explaining the lesson to the students.
4. They have already finished the project.
5. The chef was preparing dinner when the guests arrived.
答え:
1. A new bridge was built across the river by them.
2. The room will be cleaned later by someone.
3. The lesson is being explained to the students by the teacher.
4. The project has already been finished by them.
5. Dinner was being prepared by the chef when the guests arrived.
条件文
タイプ0 (Type 0): 明らかな事実を表す。
構造:
If + S + V (現在形), S + V (現在形)
例: If you heat ice, it melts. (もし氷を熱すると、それは溶けます)
タイプ1 (Type 1): 未来に起こり得る条件を表す。
構造:
If + S + V (現在形), S + will + V
例: If it rains, we will stay home. (もし雨が降れば、私たちは家にいます)
タイプ2 (Type 2): 現在の非現実的な条件を表す。
構造:
If + S + V (過去形), S + would + V
例: If I were you, I would study harder. (もし私があなたなら、もっと勉強するでしょう)
タイプ3 (Type 3): 過去の非現実的な条件を表す。
構造:
If + S + had + V-ed/irregular verb, S + would have + V-ed/irregular verb
例: If he had known, he would have come. (もし彼が知っていたら、彼は来たでしょう)
練習問題
条件文を完成させましょう。
- If I find your book, I ___ (return) it to you.
- If you ___ (study) harder, you would get better grades.
- If they had known about the party, they ___ (come).
- If she ___ (not be) so busy, she would join us.
- If you ___ (see) him, tell him to call me.
答え:
- If I find your book, I will return it to you. (もし私があなたの本を見つけたら、返します)
- If you studied harder, you would get better grades. (もしもっと勉強したら、もっと良い成績が取れるでしょう)
- If they had known about the party, they would have come. (もし彼らがパーティーについて知っていたら、来たでしょう)
- If she were not so busy, she would join us. (もし彼女がそんなに忙しくなければ、私たちに参加するでしょう)
- If you see him, tell him to call me. (もし彼に会ったら、電話するように言ってください)
間接話法
使い方
- 他人の発言や意見を再現する方法です。
例: “I need a credit card tomorrow,” said Tim.
=> Tim said that he needed a credit card the next day.
- 間接話法によく使われる動詞: say, tell, ask,…
構造
直接話法から間接話法に変換する際の構造
- 動詞の変換(元の文の時制に対して過去形に戻す)
| 直接引用の時制 | 間接引用の時制 |
|---|---|
| Present simple | Past simple |
| Present continuous | Past continuous |
| Present perfect | Past perfect |
| Present perfect continuous | Past perfect continuous |
| Past simple | Past perfect |
| Past continuous | Past perfect continuous |
| Past perfect | Past perfect |
| Past perfect continuous | Past perfect continuous |
| am/is/are going to | was/were going to |
| will | would |
| can | could |
| must/have to | had to |
| may | might |
- 時間や場所を示す語句の変換
| 直接引用文 | 間接引用文 |
|---|---|
| here | there |
| now / at the moment | then / at that moment |
| tomorrow | the next day, the following day |
| tonight | that night |
| next week / month / year | the following week / month / year,the next week / month / year |
| yesterday | the day before, the previous day |
| last week/ month / year | the previous week / month / year,the week / month / year before |
| ago | before, previously |
問題
以下の文を直接引用から間接引用に変換してください。
- “I am going to the party,” she said.
- “I will finish the report by tomorrow,” he said.
- “We have been waiting for hours,” they said.
- “They are watching a movie,” he said.
- “She has already eaten lunch,” he said.
回答
- She said that she was going to the party.
- He said that he would finish the report by the next day.
- They said that they had been waiting for hours.
- He said that they were watching a movie.
- He said that she had already eaten lunch.
関係節
- 使用法: 文に追加情報を提供するために主語の後に置かれる節です。
例: Do you know the year when the first action film was made? (最初のアクション映画が作られた年を知っていますか?)
注意点
- これらの後に関係代名詞が来る場合、関係節を省略することができます。
例: Rosie, (who is) the girl next door, usually gives me a lot of free food. (隣の家の女の子ロージーは普段私にたくさんの無料の食べ物をくれる)
- これらの後に動詞が来る場合、関係代名詞を省略することはできません。
例: I admired Jude Law, who always works hard on his films. (私はいつも映画に熱心に取り組むジュード・ロウを尊敬している)
- 関係節の前には「which」と「whom」のみが使われます。
例: Charlie Chaplin was a comic genius who all comedians owe a great deal to. (チャーリー・チャップリンは、すべてのコメディアンが多大な負債を感じているコミックの天才でした)
- 関係節の後には「that」を使わないでください。
例: My colleague Tim, that who often goes to work by train, often arrives 10 minutes late. (私の同僚ティムは、通勤でよく電車に乗るが、しばしば10分遅れて到着する)
- 「which」は前の文全体の情報を置き換えるために使用できます。
例: She got a really low score on her Math test, which surprised everyone else in the class. (彼女は数学のテストで非常に低いスコアを取得しました、それはクラスの他の誰もが驚いたことです)
- 関係節内で主語を繰り返さないでください。
例: This is the man who he created the World Wide Web. (これはインターネットを作成した男性です)
定義的関係節と非定義的関係節
| 関係節 | 定義形 | 不定形 |
|---|---|---|
| 使い方 | この対象と他の対象を区別する | 対象に追加情報を提供する |
| 関係節の情報の種類 | 重要で省略できない | 重要でなく省略可能 |
| 構造 | 関係節間にコンマがない構造 | 関係節間にコンマがある構造 |
| 特徴的な特徴 | 主語が: 固有名詞, 所有格 (my, your, etc.)this/that/these/those, 特定のもの | |
| 例 | He has two daughters. The daughter who travels a lot is a journalist. | He has a daughter. The daughter, who travels a lot, is a journalist. |
問題
空欄に適切な関係節を入れなさい。
- The man __________ is talking to Mary is her brother.
- The car __________ I bought last week is blue.
- The book __________ cover is red is mine.
- The house __________ we visited yesterday is very old.
- The restaurant __________ we had dinner last night was excellent.
回答
- who
- that
- whose
- that
- Where
欠けている動詞
モダル動詞は、英語で特定の意味(可能性、意志、助言、要求、条件など)を表現する特別な動詞グループです。以下は最も一般的なモダル動詞のリストです。
- Can: 可能性や何かをする能力を表現する。
例: I can speak English (私は英語が話せます)
- Could: 通常、過去の能力や行動を表現するために使用される。
例: When I was younger, I could run very fast. (若い頃はとても速く走れました)
- May: 許可や可能性を表現する。
例: You may leave the room now. (今すぐ部屋を出ても構いません)
- Might: “may”と同様ですが、通常は不確実な可能性を表現する。
例: It might rain tomorrow. (明日は雨が降るかもしれません)
- Must: 必要性や規則を表現する。
例: You must wear a seatbelt in the car. (車の中ではシートベルトを着用しなければなりません)
- Should: 助言や適切さを表現する。
例: You should study for the exam. (試験のために勉強すべきです)
- Ought to: “should”と同様ですが、通常は提案や個人的な意見を表現する。
例: You ought to apologize for what you said. (あなたが言ったことに対して謝るべきです)
- Shall: 通常は提案や計画を表現する。主に英国英語で使用される。
例: Shall we go for a walk? (散歩に行こうか?)
- Will: 将来の行動や突然の決定を表現する。
例: I will call you later. (後であなたに電話します)
問題
- I’m not sure if I __________ come to the party tomorrow.
- You __________ ask for permission before using the equipment.
- He __________ finish the project on time if he works hard.
- We __________ go to the beach if the weather is nice.
- She __________ stay with us for a few days.
回答
- I’m not sure if I can come to the party tomorrow.
- You should ask for permission before using the equipment.
- He might finish the project on time if he works hard.
- We might go to the beach if the weather is nice.
- She could stay with us for a few days.
前置詞
英語の前置詞は、「in」、「on」、「at」、「for」、「with」、「about」、「to」、「from」などのような単語です。これらは通常、位置、時間、方法、または目的の関係を示すために使用されます。以下は英語で前置詞を使用するいくつかの例です。
場所に関して:
- I live in a small town.
- The book is on the table.
- The cat is hiding under the bed.
時間に関して:
- The party is on Saturday.
- I have a meeting at 3 o’clock.
- We will meet in the morning.
方法に関して:
- She paid for the groceries.
- I sent an email to my friend.
- He went to school by bus.
目的に関して:
- She is studying for her exam.
- He is excited about his new job.
- We are going to the park for a picnic.
問題
- She is interested __________ learning French.
- They are going to the beach __________ the weekend.
- I will meet you __________ the café at 7 PM.
- The cat is hiding __________ the bed.
- We have been friends __________ childhood.
- The book is __________ the table.
- He is waiting __________ the bus stop.
- She lives __________ a small town.
- They are traveling __________ Europe next month.
- The party will start __________ 8 o’clock.
回答
- in
- for
- at
- under
- since
- on
- at
- in
- to
- At





