So, you’ve decided to take on the challenge of learning Chinese. Congratulations! You’re about to embark on a journey into one of the world’s most fascinating and widely spoken languages. But hold on, you might be thinking, isn’t Chinese super difficult? Well, fear not, because, in this guide, we’re going to break down the process into seven easy steps to help you get started on your Chinese learning adventure.
Why Learn Chinese?
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty, let’s talk about why learning Chinese is such a great idea. With over a billion native speakers worldwide, Chinese is not only the most spoken language globally but also a key language in international business, travel, and culture. Whether you’re interested in exploring China’s rich history and culture, expanding your career opportunities, or simply challenging yourself with a new skill, learning Chinese opens up a world of possibilities.
Addressing Common Concerns
Now, I get it. Learning Chinese can seem daunting at first, especially if you’re coming from a non-tonal language like English. But trust me, with the right approach and a bit of patience, anyone can learn Chinese. The goal of this article is to demystify the process and provide you with practical tips and resources to make your learning journey as smooth as possible.
Step 1: Understanding Chinese Basics
Characteristics of Chinese
So, what sets Chinese apart from other languages? Well, for starters, Chinese is a tonal language, which means that the pitch or tone in which a word is spoken can change its meaning entirely. Imagine saying “ma” with a rising tone versus a falling tone – they mean completely different things! Additionally, Chinese characters, though visually complex, follow a systematic structure based on radicals and basic strokes.
Role of Tones
Now, don’t let tones intimidate you. While mastering tones does require some practice, it’s entirely achievable with consistent effort. One strategy is to associate each tone with a particular gesture or image to help remember its pronunciation. For example:
First tone (flat tone): The first tone is high and flat, with a steady pitch. It doesn’t rise or fall. For example, the word “喝” (hē) means “to drink,” and “天” (tiān) means “sky.”
Second tone (rising tone): The second tone starts low and rises. It’s indicated by a rising dash above the vowel. For instance, “忙” (máng) means “busy,” and “来” (lái) means “to come.”
Third tone (dip tone): The third tone starts mid-range, dips down, and then rises. It’s like a question mark in pitch. Words like 好 (hǎo) for “good” and “马” (mǎ) for “horse” have this tone.
Fourth tone (falling tone): The fourth tone is sharp and falls abruptly. It conveys emphasis or urgency. Examples include “骂” (mà) for “to scold” and “四” (sì) for “four”.
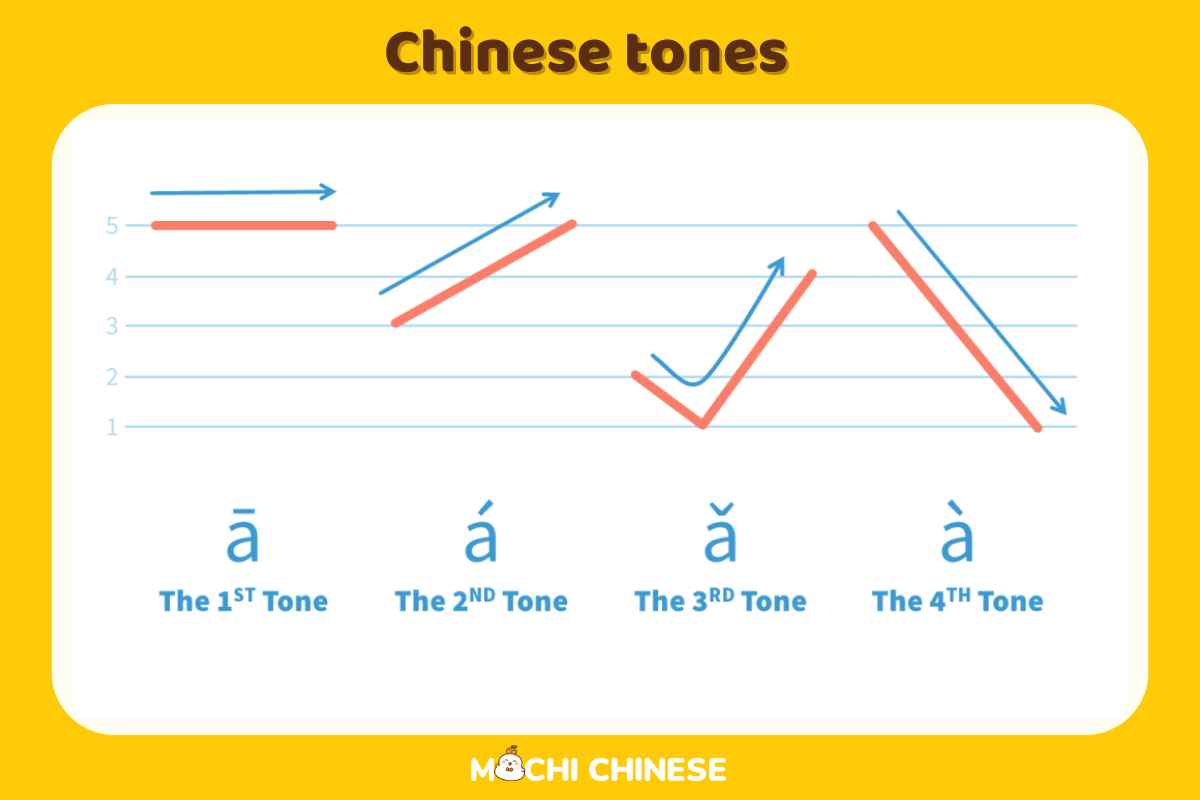
Fifth tone (neutral tone): The fifth tone is neutral and doesn’t have a fixed pitch. It occurs in unstressed syllables, such as the particle “吗” (ma) used in questions
Step 2: Start with Pinyin
Introduction to Pinyin
Pinyin serves as the bridge between the sounds of Chinese and the Roman alphabet, making it an essential tool for beginners. It’s essentially a system of phonetic transcription that helps you pronounce Chinese words accurately.
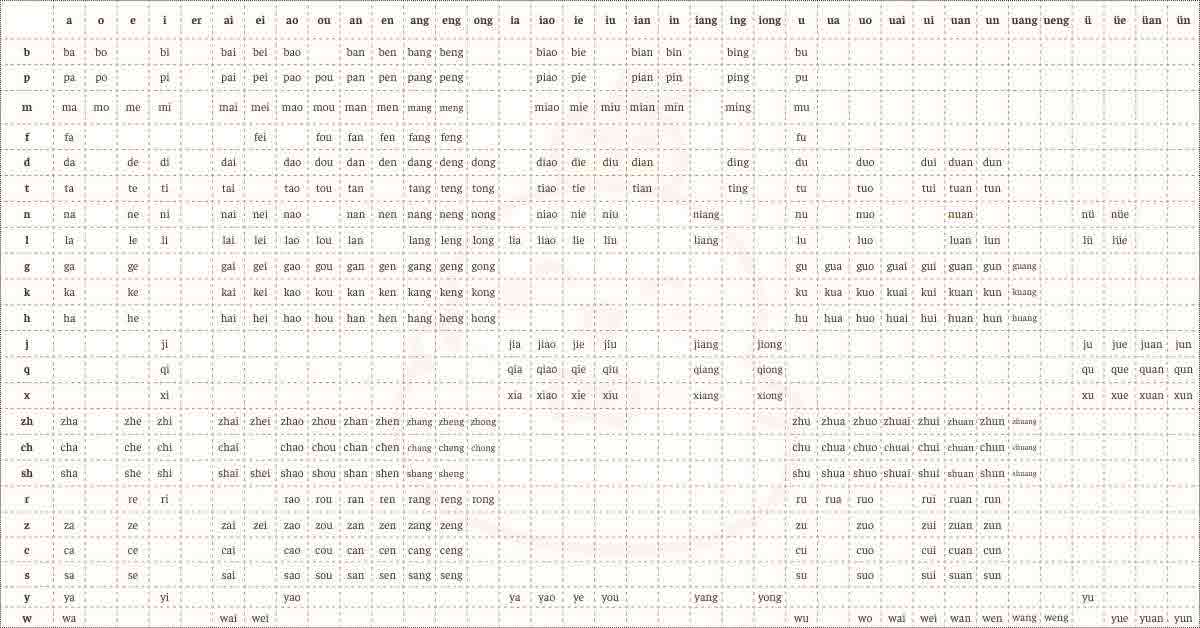
Mastering Pronunciation
To nail down your pronunciation, start by familiarizing yourself with the sounds of Pinyin. Pay close attention to the subtle differences in tones and practice speaking aloud regularly. Apps like Mochi Chinese can be incredibly helpful for expanding your vocabulary simultaneously. The app has sounds in each flashcard when learning new words and can be listened to repeatedly in interactive games during the learning process for better pronunciation.
Step 3: Learn Basic Characters
Importance of Characters
While Pinyin is great for pronunciation, it’s the characters that give Chinese its unique identity. Understanding radicals and basic strokes is key to unlocking the world of Chinese characters.
Memorization Strategies
Memorizing characters might seem daunting, but fear not – there are plenty of effective strategies to help you along the way. Spaced repetition systems (SRS) and mnemonic devices can work wonders in cementing characters into your long-term memory. Apps like Mochi Chinese offer comprehensive resources and practice exercises to support your learning journey. Moreover, the Golden Time technique in Mochi Chinese can remind you to revise your vocabulary, which will be an effective way to memorize all new words.
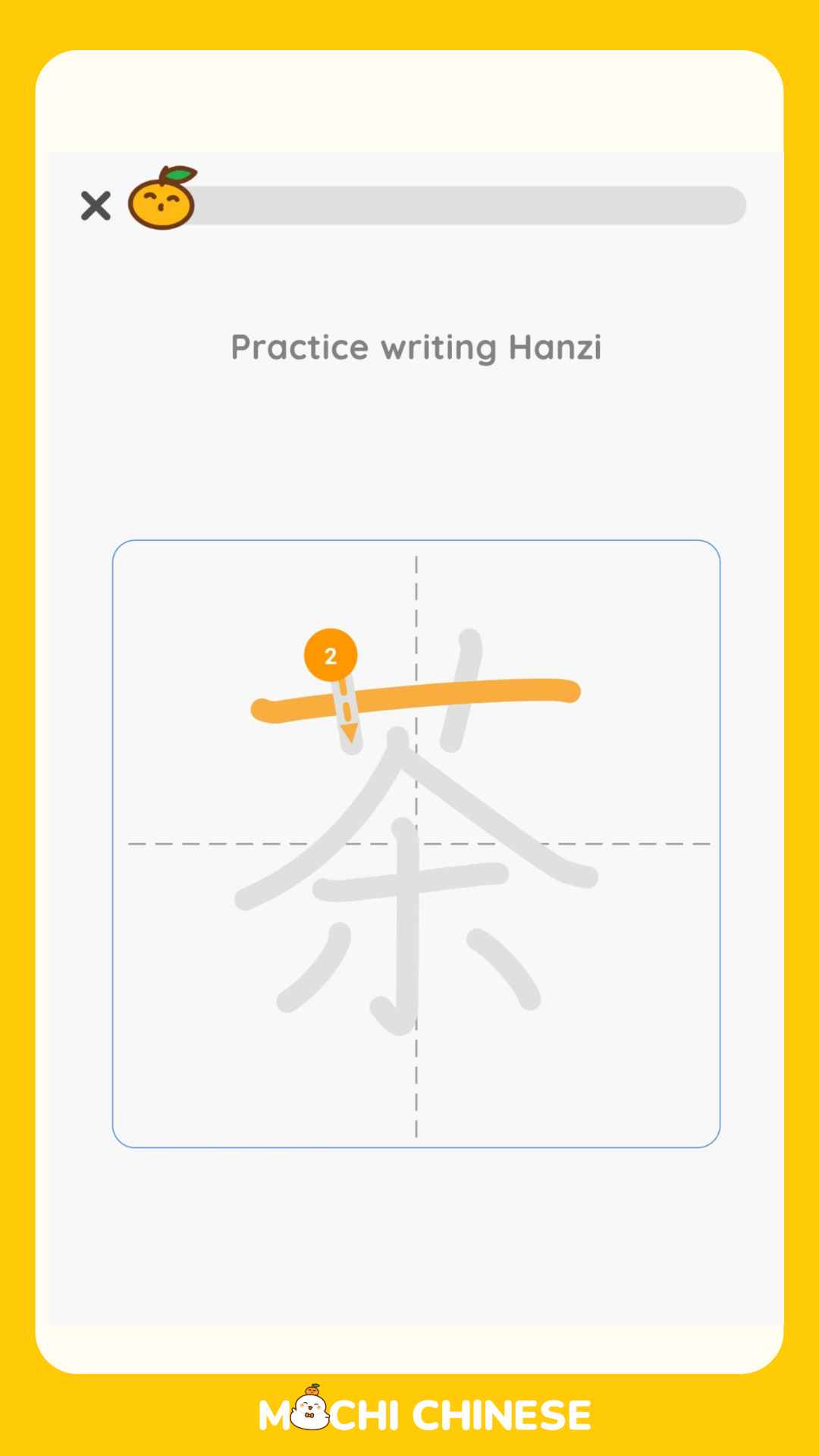
Writing Practice
Regular writing exercises are essential for reinforcing character memorization and improving overall fluency. Many language learning apps, including Mochi Chinese, offer interactive writing modules that allow you to practice stroke order and composition in a structured environment.
Step 4: Develop Listening and Speaking Skills
Listening Exercises
Expose yourself to as much Chinese media as possible, whether it’s songs, podcasts, or TV shows, such as 乘风2024 Ride the Wind, Keep Running,… Start with simpler content designed for language learners and gradually work your way up to more complex material.
Speaking Practice
Don’t be afraid to speak up! Practice speaking Chinese whenever you get the chance, whether it’s with native speakers, language exchange partners, or even just talking to yourself. Structured speaking drills and language exchange platforms can provide valuable opportunities for real-time practice and feedback.
Step 5: Expand Your Vocabulary
Thematic Vocabulary
Rather than learning random words, focus on building vocabulary around specific themes or topics such as greeting, time, weather,… You can refer to the available vocabulary topic of the Mochi Chinese web version. This not only makes learning more efficient but also enhances retention and practical usage.
Contextual Learning
Learn vocabulary in context by using example sentences and engaging in real-life interactions. Try to incorporate new words into your daily conversations and activities to reinforce your understanding.
Step 6: Engage with Cultural Elements
Cultural Understanding
Understanding Chinese culture goes hand in hand with language proficiency. Take the time to explore traditional customs, festivals, and social norms to deepen your appreciation of the language.
Cultural Activities
Immerse yourself in Chinese culture by participating in cultural events, joining online communities, or even travelling to China if you have the opportunity. The more you engage with the culture, the more natural your language-learning experience will become.
Step 7: Stay Consistent and Motivated
Routine Practice
Consistency is key when it comes to language learning. Set aside dedicated time each day to practice Chinese, whether it’s reviewing vocabulary, listening to podcasts, or having conversations with native speakers.
Motivational Tips
Stay motivated by setting achievable goals, celebrating your progress, and connecting with other learners. Remember, learning a language is a marathon, not a sprint, so be patient with yourself and enjoy the journey.
Conclusion
Congratulations, you’ve made it through the seven steps to kickstart your Chinese learning journey! By understanding the basics, mastering pronunciation, and engaging with Chinese culture, you’ve laid a solid foundation for your language skills. Remember to stay consistent, stay motivated, and most importantly, have fun along the way. Learning Chinese may have its challenges, but the rewards are boundless. So, what are you waiting for? 加油! (Jiāyóu! – Let’s go!)





