Discover why Japanese is perceived as difficult to learn and explore effective strategies for beginners. From mastering Kanji to navigating grammar, learn how dedication and structured learning can lead to success in Japanese language acquisition.
Is Japanese hard to learn?
Is Japanese hard to learn? This is a common question among aspiring language learners. The answer is multifaceted and depends on various factors, including linguistic differences, cultural nuances, and individual learning styles. Japanese is hard to learn due to its complex writing systems: Hiragana, Katakana, and Kanji, and its distinct grammar structure: Hiragana, Katakana, and Kanji, and its distinct grammar structure. Additionally, understanding cultural contexts and idiomatic expressions can be daunting. However, with dedication, consistent practice, and effective learning strategies, acquiring proficiency in Japanese is entirely achievable. The journey may be challenging, but it is also rewarding, offering deep insights into a vibrant culture.

Why do people think Japanese is hard?
There are several reasons why Japanese Japanese is perceived as hard to learn. Let’s explore the main challenges:
Japanese Writing system
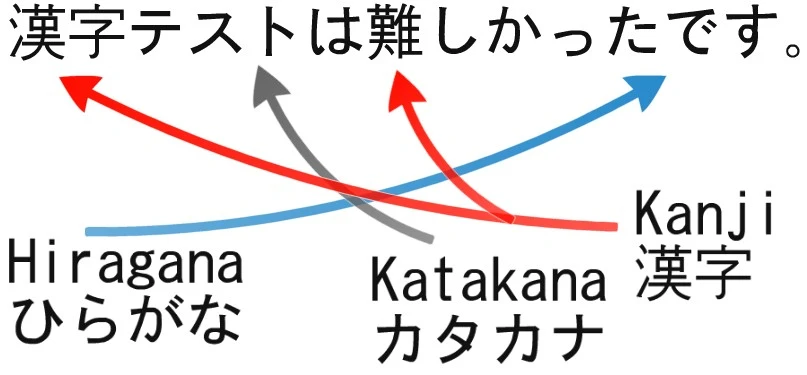
One of the primary reasons behind the perceived difficulty of Japanese is its intricate writing system, which consists of three different scripts: Hiragana, Katakana, and Kanji. Hiragana and Katakana are syllabaries, each with 46 basic characters representing different sounds. Kanji are logographic characters borrowed from Chinese, each representing a word or a meaningful part of a word. Mastering each script requires time and effort.
Kanji
Kanji is often cited as the most difficult aspect of learning Japanese. There are thousands of Kanji characters, each with multiple readings and meanings. To achieve basic literacy, learners must know at least 2,000 Kanji characters. Moreover, the complexity of Kanji lies in its stroke order, the multiple ways of reading a single character (on’yomi and kun’yomi), and the need to understand the context in which each reading is used.
Japanese Grammar
Japanese grammar is quite different from English and other Indo-European languages. The sentence structure follows a subject-object-verb order, and particles indicate the grammatical function of words.
Additionally, verb conjugations and politeness levels add layers of complexity. For example, verbs change not only for tense but also to convey respect or humility, which is not a common feature in many other languages.
In Japanese, the verb “to do” is “する” (suru). Here’s how it changes:
Plain Form (Informal):
- Present tense: する (suru) – “do”
- Past tense: した (shita) – “did”
Polite Form:
- Present tense: します (shimasu) – “do”
- Past tense: しました (shimashita) – “did”
Humble Form (謙譲語 – Kenjougo):
- Present tense: いたします (itashimasu) – “do”
- Past tense: いたしました (itashimashita) – “did”
Honorific Form (尊敬語 – Sonkeigo):
- Present tense: なさいます (nasaimasu) – “do”
- Past tense: なさいました (nasaimashita) – “did”
In this example, する (suru) is the basic verb. When speaking politely, it changes to します (shimasu). When using a humble form to show respect for the person you are talking to, it changes to いたします (itashimasu). When using an honorific form to show respect for the person acting, it changes to なさいます (nasaimasu). This complexity of verb conjugation to convey levels of politeness and respect is unique and not common in many other languages.
Honorifics
The use of honorifics, known as “敬語” (Keigo), is essential for showing respect and understanding social hierarchy in Japanese. There are various levels of politeness and honorific expressions, which can be confusing for beginners but are crucial for effective communication. Misusing Keigo can lead to misunderstandings or perceived disrespect, making it an important aspect to master for anyone serious about speaking Japanese well.
Tips to learn Japanese more easily
While Japanese is hard to learn, there are effective strategies to make the learning process smoother. Here are some tips for beginners:
Tips for Kana
Practice Daily: Consistency is key so spend a few minutes every day practicing Hiragana and Katakana. Regular practice helps solidify your knowledge and makes it easier to retain the characters.
Use Mnemonics: Develop memorable associations or stories for each character to aid in recall. Mnemonics can be a powerful tool to make learning more engaging and effective.
Flashcards: Utilize both physical and digital flashcards to reinforce your memory. Reviewing these flashcards frequently will help reinforce your recognition and recall of Kana characters, ensuring they become second nature over time.
You should try MochiKana – Learn Hiragana to learn Hiragana characters from basic to advanced. MochiKana helps you memorize the Japanese alphabet in just one week by reminding you to review at “Golden Time”. It is designed especially for starters with step-by-step learning paths. MochiKana has not only complete learning games, but also practice tests that improve your memorizing level.
Tips for Kanji
Start with common Kanji: Begin with the most frequently used Kanji characters to lay a solid foundation. These basic characters are essential for daily communication and appear frequently in everyday texts. For instance, start with Kanji characters like 日 (nichi/hi, meaning “day” or “sun”), 本 (hon, meaning “book” or “origin”), 人 (hito/jin, meaning “person”), and 学 (gaku, meaning “study” or “learning”). These characters are commonly used in everyday words and phrases, such as 日本 (Nihon, “Japan”), 先生 (sensei, “teacher”), and 学生 (gakusei, “student”). By mastering these basic Kanji, you will build a strong foundation for understanding and communicating in Japanese.
Use Learning Apps: Using learning apps like MochiKanji can greatly enhance your efficiency in mastering Kanji.
MochiKanji enhances learning with spaced repetition, mnemonic aids, and interactive games. It helps you set achievable goals, like learning 100 words monthly, making Kanji more manageable. The app also provides a supportive community, making your Japanese learning journey smoother and more enjoyable.
Practice Writing: Regularly practice writing Kanji to enhance retention and stroke order accuracy. Dedicate daily time to write each character multiple times, focusing on their structure. Use grid paper for guidance and consistency. Writing helps reinforce memory, making it easier to recall characters and recognize patterns in more complex Kanji.
Tips for Grammar
Structured Learning: When it comes to mastering grammar, following a structured curriculum or textbook can be immensely helpful. These resources are designed to introduce grammar rules and concepts systematically, allowing you to build your knowledge from the ground up. Start by familiarizing yourself with the basic sentence structure, which typically follows the pattern of subject-object-verb (SOV). Additionally, pay close attention to the use of particles, as they play a significant role in conveying meaning and nuance in many languages.
Understand Conjugations: Verbs and adjectives are essential components of any language, and understanding how to conjugate them is key to expressing yourself accurately. Spend time studying the conjugation rules for different verbs and adjectives, paying special attention to how they change depending on tense, mood, and politeness level. Mastery of conjugations will give you the flexibility to communicate effectively in various contexts.
Practice Exercises: As with any skill, practice is essential for improving your grammar proficiency. Seek out grammar exercises and drills that target specific areas of difficulty or focus on particular grammar concepts. Repetition is key here, as it helps reinforce your understanding and solidify your grasp of grammar rules. Don’t shy away from challenging exercises—embracing them will only accelerate your progress.
Language Partners: One of the most effective ways to apply grammar concepts in real-life situations is by practicing with native speakers or language exchange partners. Engaging in conversations, both spoken and written, provides invaluable opportunities to put your grammar knowledge into action and receive immediate feedback. Don’t hesitate to seek out language partners who can help you navigate the nuances of grammar usage while also immersing you in the cultural context of the language. Remember, language learning is as much about communication as it is about grammar, so embrace every opportunity to engage with others in your target language.
Additional Tips for Beginners
Immerse Yourself: Surround yourself with Japanese by listening to Japanese music, watching anime or Japanese dramas, and reading manga or Japanese books. Immersion helps in picking up natural expressions and improves listening skills. By exposing yourself to authentic Japanese content, you’ll become more familiar with the language’s nuances and rhythms.
Join Language Communities: Participate in online forums or local language exchange groups. Engaging with a community can provide support, motivation, and practical experience. By interacting with native speakers or fellow learners, you’ll have opportunities to practice your Japanese in real-life situations and receive feedback from others.
Set Realistic Goals: Set small, achievable goals to keep yourself motivated. Celebrate your progress to stay encouraged. Whether it is mastering a specific grammar point, memorizing a set number of vocabulary words, or holding a short conversation in Japanese, setting realistic goals helps you track your progress and maintain momentum in your language-learning journey.
So, Is Japanese hard to learn?
While Japanese is hard to learn, understanding the reasons behind its perceived difficulty and implementing effective learning strategies can significantly enhance your progress. By embracing the complexities of the Japanese language and incorporating targeted tips for Kana, Kanji, and grammar, beginners can navigate their learning journey with confidence and success. Remember, perseverance and consistent effort are key to mastering Japanese.
FAQs
How long does it realistically take to learn Japanese?
The time it takes to learn Japanese can vary widely depending on several factors, including your prior language experience, the intensity of your study, and the resources you use. For an average learner dedicating a few hours a week, reaching a basic conversational level may take around 1-2 years. Achieving fluency, including reading and writing proficiency, might take 3-5 years of consistent study and practice. Intensive language programs and immersion experiences can accelerate this process. The Foreign Service Institute (FSI) estimates that it takes approximately 2,200 class hours to reach professional working proficiency in Japanese.
Is learning Japanese difficult?
Learning Japanese can be challenging, particularly for native speakers of English or other non-Asian languages. Key difficulties include:
- Complex Writing System: Japanese uses three scripts—Hiragana, Katakana, and Kanji—where Kanji (Chinese characters) can be particularly daunting due to the need to learn thousands of characters.
- Grammar and Sentence Structure: Japanese grammar is quite different from English, with a subject-object-verb (SOV) order, which can be confusing for beginners.
- Pronunciation and Intonation: Japanese has relatively few sounds compared to English, but pitch accent can affect meaning and is crucial for correct pronunciation. Despite these challenges, many learners find Japanese to be rewarding and engaging, especially with the right resources and practice strategies.
Is Chinese or Japanese harder?
The difficulty of learning Chinese versus Japanese depends on various factors, including your native language and learning style. Generally:
- Chinese: Mandarin Chinese is known for its tonal nature, where pitch changes can alter word meanings, and it uses a large number of characters (Han characters). The grammar is relatively straightforward compared to Japanese, but the tones and characters can be difficult for learners.
- Japanese: Japanese has a complex writing system with three scripts and intricate grammar rules. The lack of tones in Japanese may make it easier to pronounce compared to Chinese, but mastering Kanji and understanding the subtle nuances in grammar can be challenging. Ultimately, the perceived difficulty of each language is subjective and can vary based on personal strengths and learning preferences.
Can an average person learn Japanese?
Yes, an average person can learn Japanese with dedication and consistent effort. Success in learning Japanese depends on:
- Regular Practice: Consistent study and practice are key to making progress.
- Effective Resources: Using a combination of textbooks, language apps, and immersion opportunities can enhance learning.
- Motivation and Patience: Maintaining motivation and being patient with the learning process are crucial. Setting realistic goals and celebrating small achievements can help sustain interest and progress. Many learners from diverse backgrounds have successfully learned Japanese, proving that with the right approach, it is achievable for the average person.